All you need to know about SCADA and PLC systems
The SCADA system is the heart and soul of textile machine automation. In this post we take an in-depth look at this system in the context of the textile industry.
Software is the basis of all industrial automations in any sector. After classifying the 3 types of software that can be found in the textile industry, we’ve dedicated a couple of articles detailing the importance of having an MES software to run the planning of the entire production process and we also dedicated an article to find out why an ERP management system is necessary.
All of the above cannot be possible without automating a machine with a PLC connected to a SCADA system. We could say that this is the soul of automation and without it, nothing would make sense. That’s the reason why we have created a post explaining what a SCADA and PLC system is and its usage in textile sector. Let’s start!
What is an industrial PLC?
A PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) is an industrial component which is installed in the control panel of the machines to generate input signals and to control the output ones. Hence, we can say the purpose of the PLC is to send signals and parameters. Both signals come from a higher software layer, the SCADA system.

What is a SCADA system?
SCADA stands for Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition. A bidirectional system that supervises and controls the acquisition of data from the machine it obtains and through which we can also send commands with orders. This system consists of the following elements:
- HMI: Commonly referred to as controller. It is the interface that connects the person with the machine presenting the data through a monitoring system, controlling the actions through a touch screen.
- PLC: Commonly referred to as programmable logic controllers, these are used in the system as field devices.
- Network or communication system: It is in charge of establishing the connectivity between the MES and the PLCs. For this purpose, it uses connections via modem, Ethernet, Wifi or fiber optics.
- Sensors: Devices that act as detectors of physical or chemical quantities, called instrumentation variables, and convert them into electrical variables or signals.
- Actuator: A mechanical device that is used to act or provide motion on another mechanical device.
Generally, this system is installed in the electrical panel of the automated machine, as in the case of dyeing and finishing machines. In weaving, they are much more flexible and can be found close to the machine, but not necessarily integrated into the control panel.
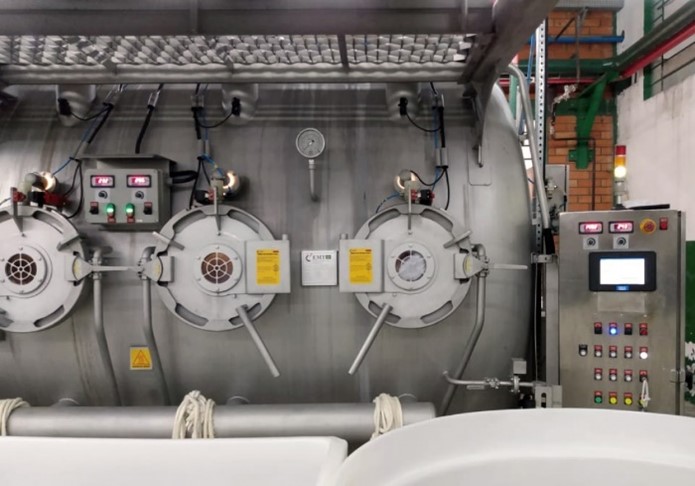


This type of automation can also be found in auxiliary textile machines such as, dosing systems or color kitchens, and performs the same function: sending orders to the machine that are executed through the PLC.
How does SCADA system work together with an industial PLC?
The SCADA software is custom designed to automate industrial processes since must be adapted to the particular functionalities of each automated machine. Therefore, we require flexible and customizable software accordingly.
Thus, we must make a list of all the functions, to assign input and output signals through the PLC. The data and execution of the functions will be visualized through a synoptic with which we can interact.
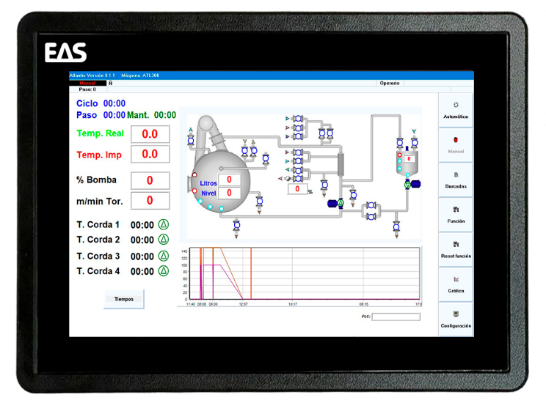
As shown in the photo, the synoptic corresponds to a dyeing jet. In it we can appreciate the level systems of the machine, the different valves, temperature, time, and we have buttons to execute functions previously assigned and properly programmed.
To give a practical example: Let’s imagine that we need to fill the machine with 100 liters of water and that it is programmed in the function 20. When introducing it in the controller this one will send the signal to the PLC that will activate the valve of water filling until obtaining the wished level.
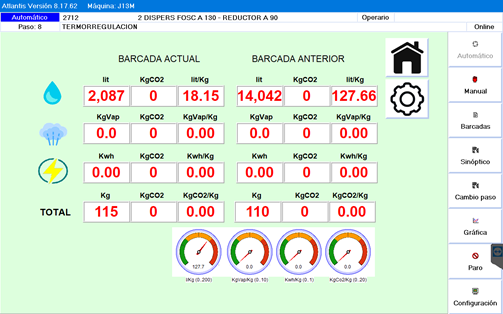
SCADA system also allows us to extract data from the machine and calculate the different consumptions used in manufacture. This real-time data will help us to reorganize the different manufacturing processes and adapt them towards more sustainable practices.
Connections with an MES and ERP system
This system does not make sense if it’s not connected to a specialized MES system. SCADA-PLC system is the first layer of software to be applies to textile automations, but to analyze and plan this extracted data we need two higher layers of software.
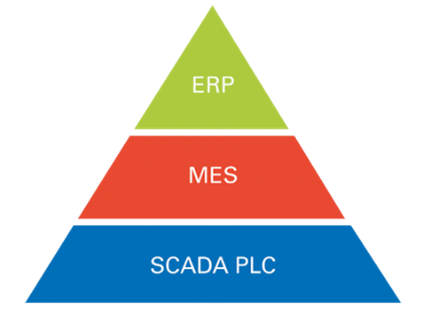
MES system is in charge of managing and centralizing all the data obtained from the production machines in real time to devise production plans.
At EAS we have developed InfoTint, our own specialized MES system for the textile industry. A multi-user system that includes the laboratory control, recipe and process management connecting with the whole machinery park to execute functions, cycles and recipes developed in a simple and easy way.
The ERP management system is one level above. As specialists in the textile industry, we have designed TexDrive: an ERP which connects to the production plant designed to cover all the demands of the sector. Furthermore, it has the capacity to manage the complete roadmap of each production batch.
TexDrive unifies the various company departments such as logistics and distribution, warehouse, inventory, and invoicing. In effect, it coordinates with the MES system, establishing a traceable route from raw materials, through production, all the way to the warehouse.
This pyramidal architecture makes it possible to digitize and initiate a transition to Industry 4.0, transforming a conventional textile plant with manual systems and separate departments into an interconnected and fully automated textile company.
Complete the pyramid to make the leap to industry 4.0
In conclusion, the SCADA system in combination with a PLC is the first step of an automation system. By obtaining data from the machine and connecting it to a MES and ERP system, we will gain full control of the textile plant.
Industrial digitization allows us to draw up a business plan and make far-reaching decisions based on the actual data we obtain from the production machines. These types of technological innovations in the textile industry help us to make our company more competitive and make the transition to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly industry.
If you want more information, tell us about your project, we will be happy to advise you without obligation, write to us! We also invite you to follow us on our Linkedin page.